| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | ||
| 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 |
| 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 |
| 20 | 21 | 22 | 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 |
| 27 | 28 | 29 | 30 | 31 |
- github
- RDS
- TypeScript
- ngrok
- 500
- python
- linux
- webhook
- Github Actions
- nodejs
- javascript
- deploy
- Jenkins
- Troubleshooting
- AWS EC2
- Spring
- React
- springboot
- AWS
- macbook
- EC2
- js
- MUI
- Express
- MongoDB
- error
- fastapi
- Java
- docker
- axios
- Today
- Total
BEAT A SHOTGUN
[FastAPI] MongoDB 와 연결해 CRUD api 만들기 본문
매우 간단한 CRUD 만들기를 해볼거다.FastAPI, 데이터베이스로는 MongoDB 와 연결해볼거다.MongoDB 와 연결을 위해서는 Odmantic 이라는 중간다리 ODM 이 필요하다.mysql 같은 RDB 였다면 mybatis 같은 ORM 이 필요했겠지? python 에서도 mybatis 쓰나? 모르겠다 아무튼 odmantic 이 그런 역할이라 사용할거다.
먼저 pip install odmantic 을 이용해 설치해주자.
매우 쉽지만, 매우 고된 과정이었다. 영어를 못해서.
참고
motor AsyncioMotorClient
odmantic
pymongo API Docs
pymongo readthedocs
stackoverflow
MongoDB Docs
MongoDB 기초 - 블로그
그래서 정리함.
시작👊

일단 나는 controller 로 분리해놓았기 때문에
이렇게 사용해보자.
일단 잘 연결되는지 테스트를 해볼까욤🙂?
test
# /app/main.py
from fastapi import FastAPI
from app.controller.user_controller import UserController
app = FastAPI()
user_conteroller = UserController()
@app.post("/test")
async def test()
test = await user_controller.test()
return test내일은 user 에 관한 것들을 또 main 에서 분리할 거다.
# /app/controller/user_controller.py
class UserController:
async def test(self):
return "test 성공"조악하지만 연결을 확인하기엔 충분하다.
MongoDB
먼저 소중한 우리의 secrets 만들어 MongoDB 관련 데이터를 넣어주자. root 에 넣음.
{
"MONGO_DB_NAME":"우리가 만들 데이터 이름",
"MONGO_DB_URL":"우리의 몽고DB URL"
}Mongo_DB_Name 은 우리가 만들거니까 아무거나 써도 됨.
# /app/config.py
import json
from pathlib import Path
from typing import Optional
# root 폴더로.
BASE_DIR = Path(__file__).resolve().parent.parent
def get_secret(
key: str,
default_value: Optional[str] = None,
json_path: str = str(BASE_DIR / "secrets.json")
):
with open(json_path) as f:
secrets = json.loads(f.read())
try:
return secrets[key]
except KeyError:
if default_value:
return default_value
raise EnvironmentError(f"Set the {key} environment variable")
MONGO_DB_NAME = get_secret("MONGO_DB_NAME")
MONGO_DB_URL = get_secret("MONGO_DB_URL")이제 본격적인 연결
어디서든 mongodb 를 호출할 수 있도록.
# /app/models/__init__.py
# motor - MongoDB 용 비동기 python 라이브러리
from motor.motor_asyncio import AsyncIOMotorClient
from odmantic import AIOEngine
# 소중한 Secrets.json 가져오기
from app.config import MONGO_DB_NAME, MONGO_DB_URL
class MongoDB:
def __init__(self):
self.client = None
self.client = None
def connect(self):
self.client = AsyncIOMotorClient(MONGO_DB_URL)
self.engine = AIOEngine(client=self.client, database=MONGO_DB_NAME)
print("DB 와 연결되었습니다.")
def close(self):
self.client.close()
mongodb = MongoDB()그리고 main.py 이 작동되면 바로 mongodb 를 연결하도록.
# main.py
# mongodb연결
from app.models import mongodb
...
@app.on_event("startup")
def on_app_start():
mongodb.connect()
@app.on_event("shutdown")
async def on_app_shutdown():
mongodb.close()이제 main - controller 도 됐고, db 도 연결된 거 같으니
Create
# main.py
...
@app.post("/user/create")
async def create_user(username: str = Form(), password: str = Form()):
user = await user_conteroller.create_user(username, password)
return user
username 과 password 를 Form() 형태로 받아 보내버리기.
중요한 정보기 때문에 post 로 받은거다.Request 형태로 받으면 이리저리 요리해도 byte 형태로 받아져서 Form 으로 받았다.
# user_contoller.py
# mongodb engine 을 사용해야하므로 불러오자. 나중엔 client 도 사용함.
from app.models import mongodb
...
# 회원 가입
async def create_user(self, username, password):
# 나는 dict 가 아니라 UserModel 을 만들어서 해당 모델형태로 입력했다.
user = dict(
username=username,
password=password
)
await mongodb.engine.save(user)
print(f"{username}으로 가입되었습니다.")
return create_user모로가도 들어가면 되는 거죠?만약 모델이 있다면 dict 대신 모델을 쓰고 만들어놓은 모델에 맞게 채워넣으면 되고, 없으면 dict 쓰면 되지~
Read(find)
앞서 만든 모델의 유무에 따라 사용법이 약간 달라질 거 같은데 큰 차이는 아니니 일단 해보자.
# main.py
...
@app.post("/user/find")
async def find_one(username: str = Form()):
user = await user_conteroller.find_one(username)
return userfind 메서드. 사용자들이 쓰진 않을 거지만, 다른 함수들에 사용될 수도 있으니 일단 만들어버렷
# user_controller.py
...
# 아래 pymongo 가 제공하는 find_one 이라는 메서드를 사용할 거다.
# 지금 이 find_user 메서드는 다른 메서드에서도 사용할 전체 유저 데이터를 return 하는 메서드
# 이름을 잘 못 만든 거 같긴하다. 너무 헷갈려. find_one 은 pymongo 가 제공하는 메서드임
async def find_user(self, username):
# 모델을 만들고 안 만들고는 이부분이 달라질거라 생각된다. engine 을 쓰느냐
result = await mongodb.engine.find_one(UserModel, UserModel.username == username)
print (result)
# 모델을 만들고 안 만들고는 이부분이 달라질거라 생각된다. client 를 쓰느냐
# result = await mongodb.client.database 이름.collection 이름.find_one({"username":username})
if result:
return result
else:
print("검색결과가 없습니다.")
return None
# 회원 찾기
async def find_one(self, username):
try:
result = await self.find_user(username)
if result:
# result 가 dict 타입일 때와 Model 타입일 때가 문법이 다르므로 적을 때 꼭 살펴보자.
found_user = dict(
# result 가 dict
username=result.username,
password=result.password
# result 가 Model
# username=result["username"]
# password=result["password"]
)
# 어쨋든 return 은 dict 로 할 거기 때문에 dict 에 넣어준다.
return found_user
else:
print(f"'{username}' 에 대한 검색 결과가 없습니다.")
except Exception as e:
print("Error : ", e)
return e- pymongo 가 제공하는
find_one메서드는 가장 먼저 찾은 "하나의" 문서를 돌려준다.
그 외에도find(),find_many()등이 있다.
engine 과 client 의 차이
무슨 차인지 알고 싶다.
하지만 아직 할 게 많다.
아무튼! (
아무튼무새
)engine.find_one(UserModel, UserModel.username == username) 을 하지 않고,engine.find_one(dict, UserModel.username == username) 을 하면 아래 에러가 난다.
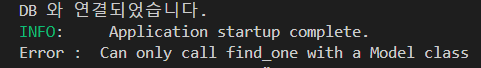
이렇게 되면 result 가 Model 타입 이 제공된다.
반면 client.database 이름.collection 이름.find_one({"username":username}) 라고 적었다면, dict 타입 으로 제공 되기 때문에 아래에서 받을 때,
- Model 타입은
result.username으로 받을 수 있고, - dict 타입은
result["username"]으로 받을 수 있다.
Update
# main.py
...
@app.post("/user/update")
async def update_user(username:str = Form(), newpassword:str = Form()):
user = await user_conteroller.update_user(username, newpassword)
return user새로운 비밀번호를 받아 교체해보자.
# user_controller.py
...
async def update_user(self, username, newpassword):
try:
result = await mongodb.client.database 이름.collection 이름.update_one(
{"username":username},
{"$set":{
"password":newpassword,
"user_update_at":datetime.now()
}}
)
return "회원 정보 수정 완료."
except Exception as e:
print("Error : ", e)
return eupdate_one으로 수정 후 반환 받을 수 있는 데이터는 많지 않다.
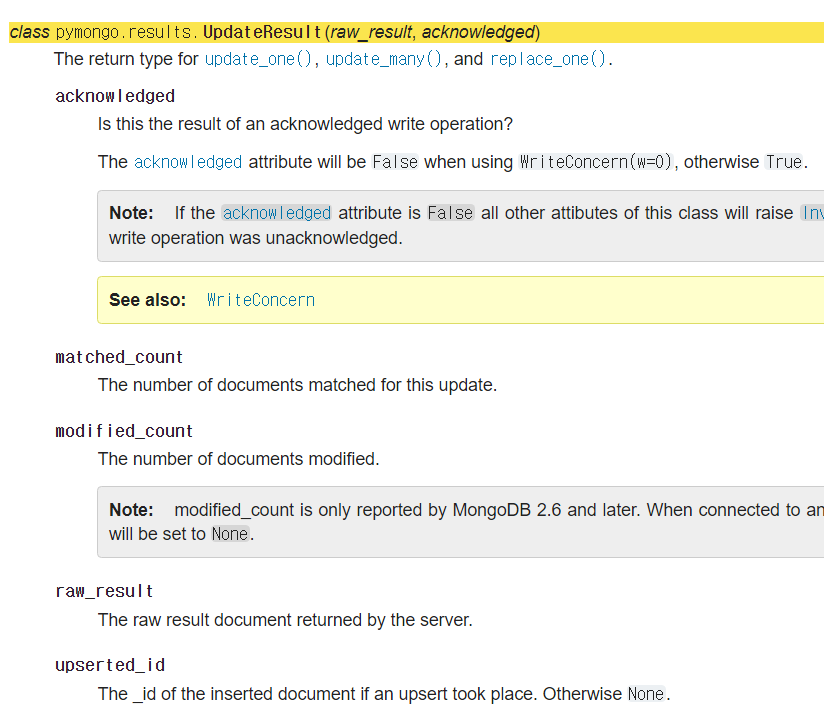
그래서 일단 수정완료 메세지가 return 되도록 했다.modified_count를 했을 때 수정된 수가0이라면 수정이 안된거고,1이라면 (update_one) 수정된거다. 상황에 맞게 사용해보도록 하자."$set"을 하지 않으면, 해당 문서 항목의 다른 데이터는 없이 적어넣은 새 데이터만 입력되니 매우매우매우매우 조심 해서 사용하자.
참고
stackoverflow , MongoDB Docs , MongoDB 기초 - 블로그
Delete
삭제도 어렵지 않다.
# main.py
...
@app.delete("/user/delete")
async def delete_user(username:str = Form(), password:str = Form()):
result = await user_conteroller.delete_user(username, password)
return result- 삭제도 비밀번호 확인해서 삭제시키자. 안그러고 싶으면 그냥 username 받기만해도 될거같다.
# user_controller.py
...
# 회원 삭제(탈퇴)
async def delete_user(self, username, matchpassword):
check_password = await self.find_user(username)
if check_password.password == matchpassword:
try:
delete_user = await mongodb.client.database 이름.collection 이름.delete_one(
{"username":username}
)
if delete_user.deleted_count == 0:
return "삭제에 실패했습니다."
else:
return f"{delete_user.deleted_count}개의 계정이 삭제되었습니다."
except Exception as e:
print("Error : ", e)
return e
else:
return "비밀번호가 틀렸습니다."delete_one혹은delete_many메서드를 하게 되면 update 와 같이 삭제된 수량을 알려준다.deleted_count
이걸 이용해서 삭제가 안되었다면 삭제에 실패했다는 말을 해준 거다.
끝
일단 이건 매우 쉬운 기본 단계다.
내가 이거 밖에 못함😉
여기서 우리는 return 값을 dict 로 만들어주고 그랬지만, api 를 만들 때 response_model 을 선언해주면서 response_modle 의 형태도 쉽게 정의할 수 있다.
무엇보다 fastapi 는 api 명세를 만들어 제공해주기 때문에(java 에서 swagger를 사용할때처럼) 매우 편리하게 프론트와 소통할 수 있다. 그래서 response model 을 어떻게 만드는 게 좋을 지 함께 고민해보면 좋을 것 같다.
- redoc
- docs

진짜 끝
아유 할 게 아직 산더미네 산더미야.
일기 끝
다시 한 번 '참고'
motor AsyncioMotorClient
odmantic
pymongo API Docs
pymongo readthedocs
stackoverflow
MongoDB Docs
MongoDB 기초 - 블로그
'LEARNING' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [R] R 설치와 R 스튜디오 설치 및 간단 사용법 - R 의 시작 (0) | 2023.03.26 |
|---|---|
| [FastAPI] main 에 때려박은 user 관련 API 분리하기(feat. FastAPI 공식 Docs) (0) | 2023.02.09 |
| [FastAPI] 가상환경에 들어가서 FastAPI 설치하기 (0) | 2023.02.05 |
| [Python] 동시성 프로래밍으로 데이터를 더 빠르게 정렬해 Excel 로 뽑아내보자 (Feat. FastAPI, aiohttp) - 2 (0) | 2023.02.03 |
| [Python] 동시성 프로래밍으로 데이터를 더 빠르게 정렬해 Excel 로 뽑아내보자 (Feat. FastAPI, aiohttp) (1) | 2023.01.29 |
